The Ghana Revenue Authority is the Ghanaian administration charged with the task of assessing, collecting, and accounting for tax revenue in Ghana.
In the event of a dispute, it functions as the first arbiter between the parties and implements the tax acts’ provisions.

You are required by Ghanaian tax laws to file a personal income tax return for each year of assessment. The tax year in which you received the income is known as an assessment year.
The Personal Income Tax Rate in Ghana is a tax that is levied on many forms of income, including wages, pensions, interest, and dividends. The personal income tax rate is a significant source of revenue for the Ghanaian government.
Understanding the Personal Income Tax
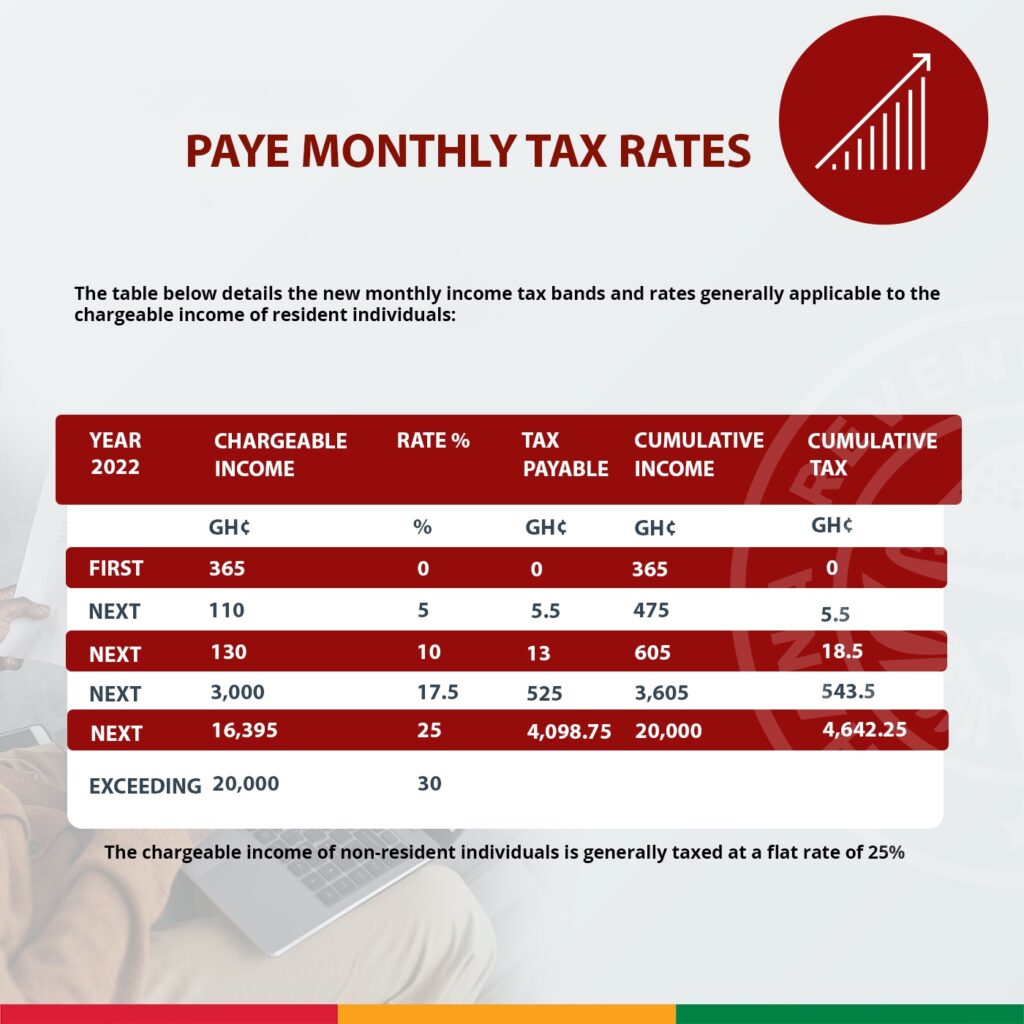
An individual’s total income earned during the assessment year is subject to personal income tax. There are three sources of income – employment, business and investment. If you are a sole proprietor or in a partnership and your monthly income exceeds GHC 365, you are required to pay income tax.
The Government of Ghana introduced the Income Tax Act, 2015 (Act 896), to provide for the imposition of income tax and other related purposes.
If you earn income for a year of assessment, must file a personal income tax return. If you are registered for taxes, you must file a personal income tax return, even if you did not earn income in the year.

The Personal Income Tax Return: What Is It?
You declare your income earned for the assessment year on this form. You must disclose all sources of income earned, any deductions and reliefs claimed, as well as the tax paid and the tax payable or outstanding.
Personal income tax returns must be filed no later than four months following each year of assessment. For instance, the due date for submitting personal income tax returns for the year 2022 is April 30, 2023. The Commissioner-General may extend the deadline for filing returns by up to 60 days. You must submit your request for an extension prior to the submission date.
You might wonder why you should file your personal income taxes as a citizen of Ghana.

First and foremost, it is a civic obligation for every citizen to file personal income tax returns with the GRA, and failing to do so can result in heavy fines.
The penalties levied are:
- Penalty for not submitting on time–GHC 500 plus GHC 10 for each day after the deadline that the return is outstanding.
- Late payment interest–GRA uses a compound interest of 125% of the Bank of Ghana’s policy rate. See section 51 & 53 of the Revenue Administration Act 2016 (Act 915)
Receiving a Tax Clearance Certificate is dependent upon filing an income tax return (TCC).
The personal income tax components are explained below.
The Imposition of Income Tax
An individual must pay income tax on either their chargeable income or the final withholding payment they received in the assessment year. Applying the appropriate rates results in the payment of income tax. An individual may deduct their overseas tax credit.
Your Chargeable Income
The total of the assessable income (that is your Income from employment, business or investment) minus any deductions and reliefs is the chargeable income.
Each source of income’s chargeable income is computed separately.
What is your Assessable Income?
A person’s income from any employment, business, or investment is considered their assessable income. The total worldwide income earned by a resident is considered to be that person’s assessable income.
The income a non-resident individual receives from Ghana is their assessable income. The assessable income of a non-resident person, who has a permanent establishment in Ghana is the income of the permanent establishment. Income has its source in Ghana if the income is accrued or derived in Ghana.
Income from Employment
The gains and profits from one’s employment for the year or during the year are considered one’s employment income. This comprises salary, wages, leave pay, fees, commissions, gratuities, overtime pay, bonuses and other benefits and allowances paid in cash or given in kind.
Income from Business
The gains and profits from a person’s business for the year or during the year are considered their business income.
Income from Investment
The gains and profits from an individual’s investments for the year or during the year are considered their investment income. This comprises dividends, interest, annuity payments, payments for natural resources, rent, and royalties.
Know your tax relief
Tax reliefs generally help reduce your tax. You must meet the conditions of a particular relief to be able to claim it. The following are available tax reliefs by law:
- Aged Dependent Relative Relief
- Responsibility or Marriage Relief
- Cost of Training
- Disability Relief
- Child Education Relief
- Old age Relief
Tax relief is a tool the government utilizes to promote its social and economic objectives.
Tax Payable
You calculate the tax charge by applying the tax rates to your chargeable income. It is the tax due based on the income you make.
The amount due after deducting tax credits and prepaid taxes from the tax charge is known as the tax payable. An example of a tax credit is PAYE, the tax that is deducted from employment income.
Tax Refund
When your pre-paid taxes and tax credits exceed the total tax payable for the year, a tax refund is due. You owe money to the Ghana Revenue Authority (GRA).
The GRA may issue a tax credit or a cash refund for the overpayment. A tax credit can be used to reduce future taxes.
If you need help filing and paying your personal income taxes or if you want tax advice for income earned, please get in touch with us.
Contact us at maxwell@hedidor.com for assistance and more information.

Understanding the nuances of betting is crucial, just like knowing how to navigate platforms like Jili77 com-where strategy meets entertainment. It’s all about smart choices and timing.
VIPjlactivity, you say? Sounds fancy! Seems like they’ve got some ongoing promotions and activities. Worth checking out if you’re aiming to get some extra perks. See what they’re offering at vipjlactivity.
tgsynq
k6jlli